For those who need a filling firmware and more complete information about the USB Downloader please visit http://guru.technosains.com/
Tuesday, November 29, 2011
AT89s51-52 and AVR USB Downloader
For those who need a filling firmware and more complete information about the USB Downloader please visit http://guru.technosains.com/
Wednesday, November 16, 2011
Rangkaian Pendeteksi Angin
 |
| Rangkaian Pendeteksi Angin |
 |
LM339 Pinout |
List Component
R1 : 100 Ohm 1/4W Resistor R2 : 470 Ohm 1/4W Resistor R3 : 10k 1/4W Resistor R4 : 100K 1/4W Resistor R5 : 1K 1/4W Resistor C1 : 47uF Electrolytic Capacitor U1 : 78L05 Voltage Regulator U2 : LM339 Op Amp L1 : #47 Incandescent lamp with glass removed (See "Notes") D1 : LED
Stepper Motor Controller using IC 4027
 |
| Stepper Motor Controller Circuit using IC 4027 |
List Componet
R1, R2 ,R3, R4: 1K 1/4W Resistor D1, D2, D3, D4: 1N4002 Silicon Diode Q1, Q2, Q3, Q4: TIP31 NPN Transistor (See Notes) TIP41, 2N3055 U1 : 4070 CMOS XOR U2 : 4027 CMOS JK Flip-Flop S1 : SPDT Switch
Notes:
1. You should be able to substitute any standard (2N3055, etc.) power transistor for Q1-Q4.
2. Every time the STEP line is pulsed, the motor moves one step.
3. S1 changes the motors direction.
 |
| 4027 CMOS JK Flip-Flop IC Pinout |
 |
| 4070 CMOS XOR IC Pinout |
Sunday, October 30, 2011
Ukuran Box Subwoofer 10"
The enclosure design and model frequency response are shown below.


Note:
- 10" 4 ohm subwoofer
- O-Audio 500 Watt plate amplifier
- Freq Response: 25Hz up to chosen x-over point.
- Overall Dimension: 21"x 12.75"x 20"
For more details on how to make it please read more http://diyaudioprojects.com/Speakers/HiVi-DIY-Subwoofer/
4,8W Class-A MOSFET Amplifier
The four resistors are 15ohm and 10W each the which I wired two in series for 30 ohms and then the two sets of 30 ohms are wired in parallel to give a total resistance of 15 ohms. These get extremely hot and burn about 30W at idle.
For more detail please read more http://diyaudioprojects.com/Solid/ZCA/ZCA.htm
LM383 - Car Audio Amplifier Circuit
Note:
That it's advised you use this with a LM383 chip Suitable heatsink.

This is one package pinout of LM383 chip, If you need more pinouts please download LM383's pdf datasheet.
Friday, June 10, 2011
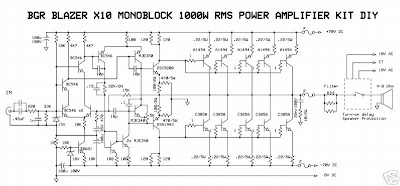
Rangkaian Power Amplifier Blazer 1000 Watt
This circuit describes an amplifier, power supply and tests procedures that are all inherently dangerous. Nothing described in this article should even be considered unless you are fully experienced, know exactly what you are doing, and are willing to take full 100% responsibility for what you do. There are aspects of the design that may require analysis, fault-finding and/or modification.
Tuesday, June 07, 2011
500 Watt Inverter 12VDC to 220VAC
Step up part of this inverter circuit using a transformer 12VCT/500VA in secondary and primary 0 - 220V. While the frequency is determined by the flip-flop which is set to 50 Hz.
Note:
- Q7, Q8 and Q7x, Q8x require heat sink.
- Output power of this dc dc converter is around 500 watts.
- An optional 40A fuse can be added in circuit to the 12V supply line.
- T1 can be a 12-CT-12V /250V/40A mains transformer.
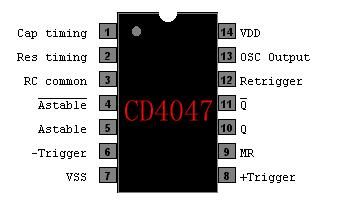
12VDC – 220VAC Inverter Using Cmos CD4047
This Circuit From: http://apowersupply.com
Thursday, May 19, 2011
Light/Dark Switch With Relay
The circuit as shown act as a light detector. Under normal conditions the resistance of the LDR is high, keeping pin 2 low. When light falls onto the LDR the resistance drops to a couple hundred ohms and triggers pin 2 high which biases the base of Q1 via pin 6 and R4 and in turn activates the relay.
The second voltage divider will settle the reference voltage. The first voltage comparator that contains the LDR, will change it's voltage according to the light level. When the voltage across the negative input of the comparator is less than the voltage to the positive input of the comparator, the output is held low. When the voltage on the negative input rises, there will be a time that it becomes greater than or equal to the positive (pre-selected) voltage, and then the output becomes high and the relay through the 2N2222 is actuated.
Refrigerator Door Alarm Circuit Using LDR
The alarm circuit enclosed into a small box is placed in the refrigerator near the lamp. With the door closed the interior of the refrigerator is in the dark, the LDR R2 presents a high resistance thus clamping IC1 by holding pin 12 high. When a beam of light enters from the opening, or the refrigerator lamp illuminates, the LDR lowers its resistance, pin 12 goes low, IC1 starts counting and, after a preset delay (20 seconds in this case) the piezo sounder beeps for 20 sec. then stops for the same lapse of time and the cycle repeats until the refrigerator door closes. D2 connected to pin 6 of IC1 allows the piezo sounder beeping 3 times per second.
Note:
- Delay time can be varied changing C1 and/or R3 values.
- Quiescent current drawing is negligible, so SW1 can be omitted.
- Place the circuit near the lamp and take it away when defrosting, to avoid circuit damage due to excessive moisture.
- Do not put this device in the freezer.
List Component:
R1 : 10K
r2 : LDR any type
R3,R4 : 100K
C1 : 10nF
C2 : 100µF/25V
D1,D2 : 1N4148
IC1 : 4060 14 stage ripple counter and oscillator IC
Q1 : BC337
BZ1 : Piezo sounder (incorporating 3KHz oscillator)
SW1 : SPST slide Switch
B1 : 3V Battery
This alarm circuit from : http://www.redcircuits.com/
Sunday, May 01, 2011
Rangkaian 11-90 hz Subwoofer Filter Using TL072 Op-Amp
6 Band Graphic Equaliser Circuit Using 741 Op-Amp
Essentially, the circuit consists of an IC 741 whose gain at various freguencies is determined by corresponding potentiometer setting.
power supply for the circuit can be derived from the amplifier / preamplifier itself. The wide rangeof supply voltage (6V-20V) makes the circuit very versatile. Power consumption is negligible.
list Component
R1,R2,R3,R4,R5,R6 : 27kΩ C1: 100n C6: 300pF
R7: 470kΩ C2: 33n C7: 100uF/16V
R8: 330kΩ C3: 10n C8: 4.7uF/16V
R9: 100kΩ C4: 3.3n C9: 47uF/16V
R10: 4.7kΩ C5: 1n IC1: 741 Op amp
R11: 4.7kΩ
VR1,VR2,VR3,VR4,VR5,VR6: 100kΩ Linear Potentiometers
Rangkaian 400W MOSFET Amplifier
Note:
- Use + /-70V 10A DC dual supply for powering the circuit.
- For L1 make 12turns of enameled copper wire on a 1cm him: plastic formers.
- use 8 x IRFP448 MOSFETs in the final stages
- Heat sink is Necessary for the MOSFETs. A 8x4x4 inch finned aluminum heat sink will do. There is no such thing as a heat sink That is too large.
Also to what the name suggests this stage converts the voltage developed in the VAS and provides all the amps required to drive at 8 or 4 ohms. 2-ohm loads are possible for several minutes at a time. In fact, I have tested more than 1600 1kW amplifier Watts RMS at 2 ohms. But that would not be recommended as a long-term exposure at all. If it is higher than the figures of the STI-amp. Power to the AV amplifier 800 The components of the power for this amplifier are as follows, and are favored A channel or a power module alone. 1 toroidal transformer with a rating of 1kVA. Primary windings are made to fit
Audio Peak Level Indicator By Op-Amp
The circuit was optimized for low current consumption as it was intended for battery operation. To achieve this, the best arrangement has proven to be the one using two different op-amp types for IC1 and IC2. In fact the LM393 IC was not operating satisfactorily as dot-mode LED driver, whereas the LM324 was unable to charge C2 in the linear way, as expected. Therefore, the final circuit is some op-amp wasting, but the small added cost will be quickly compensated by battery savings.
List Component:
R1 : 300K D1,D2,D3 : LEDs
R2 : 1M2 IC1 : LM393
R3 : 510K IC2 : LM324
R4 : 220K IC3 : 78L05
R5 : 91K SW1 : SPST Toggle or Slider Switch
R6 : 160K B1: 9V PP3 Battery
R7 : 56K
R8,R9 : 100R
R10 : 220R
C1 : 100nF
C2 : 1µF/63V
C3 : 10µF/25V
Wednesday, April 06, 2011
DC Motor Controller Circuit Using 741 Op-Amp
When VR1 is turned towards the positive supply side, the output will go positive voltage and Q1 will supply the current to the motor and Q2 will be OFF. When VR1 is turned to the negative supply side, the op-amp output switches to the negative voltage and Q1 will turn OFF and Q2 ON which reverses the rotation of the motor's direction.
Rangkaian 3V FM Transmitter
The circuit is basically a radio frequency (RF) oscillator that operates around 100 MHz. Audio picked up andamplified by the electret microphone is fed into the audio amplifier stage built around the first transistor. Output from the collector is fed into the base of the second transistor where it modulates the resonant frequency of the tank circuit (the 5 turn coil and the trimcap) by varying the junction capacitance of the transistor. Junction capacitance is a function of the potential difference applied to the base of the transistor. The tank circuit is connected in a Colpitts
So it is best to adjust it in steps of 5 to 10 degrees at each turn. So tuning takes a little patience but is not difficult. The reason that there must be at least 10 ft. separation between the radio and the FM transmitter is that the FM transmitter emits harmonics; it does not only emit on one frequency but on several different frequencies close to each other. You should have little difficulty in finding the Tx frequency when you follow this procedure.
25V Capacitor Bank for OCL Amplifier
The circuit diagram below shows how the +25V DC and -25V DC are obtained. In order to provide power supply for stereo amplifiers, a power transformer rating of 80VA with 240V/36V centre tapped secondary winding is used. The secondary output of the transformer is rectified by using four 1N5401 diodes together with 4 electrolytic capacitors to smoothen the ripple voltage. A fuse and a varistor are connected at the primary input to protect the circuit against power surge. Here you can see the circuit’sdiagram diagram

Although shown with 4,700uF filter capacitors, larger ones may be used. Anything beyond 10,000uF is too expensive, and will not improve performance to any worthwhile degree. Probably the best is to use two 4,700uF caps per side (four in all). This will actually work better than a single 10,000uF device, and will be cheaper as well.
It is essential that fuses are used for the power supply. While they will not stop the amp from failing (no fuse ever does), they will prevent catastrophic damage that would result from not protecting the circuit from over-current conditions.
Wednesday, March 23, 2011
35W Audio Amplifier Circuit by STK082
Here is a 35W audio amplifier circuit built based on single Amplifier chip STK082. This is a very simple amplifier, very easy to build and produce sound output with a fairly large power of 35 watts into 8 Ohm loads.
 This amplifier circuit is suitable for home power audio devices. The STK082 amplifier specifications might lead you to believe that it can use supply voltages of up to ±43V. but I don't recommend anything greater than ±25V if 8 ohm loads are expected, although ±30V will be fine if you can provide good heatsinking.
This amplifier circuit is suitable for home power audio devices. The STK082 amplifier specifications might lead you to believe that it can use supply voltages of up to ±43V. but I don't recommend anything greater than ±25V if 8 ohm loads are expected, although ±30V will be fine if you can provide good heatsinking.Rangkaian Audio Surround Decoder

The operation of the above circuits starts as the stereo sound signal transports surround sound information on the master volume part of the circuit. This will drive the Left channel Lch attached to Model TL072 IC1A and IC1b in which Right channel Rch is attached. The outputs on these operational amplifiers would serve as the input buffer to the following stages of the circuit. IC2C is responsible for summing up the signals from the left and right channels that will power the central loudspeaker output while IC2D is responsible for increasing the phase difference between left and right channels which is encoded in the two channels and will be fed to the rear loudspeakers. It is necessary to ensure that the negative terminals between the rear speaker is not earthed because they will simply function in parallel with the main speakers.
The output of IC2D will power regulated delay unit of audio to the rear loudspeakers. This would lead to the creation of proper sense of spacing in accordance to the size of the room. This will incorporate op-amp sound delay signal IC5 MN3004 which has 512 stages. Since IC4 MN3101 is a clocking signal, it provides timing to IC5 as it functions as an oscillator in the circuit. Variable capacitor C17 regulates the delay time in the circuit. The presence of filters in the circuit is for the purpose of preventing noise that will be produced during the process. These filters can be regulated to cut the frequencies above 8 KHz and under 100 Hz, to be able to drive the rear speaker. The rear loudspeaker is small in size because its input is encoded with a bandwidth of 100 Hz up to 8 KHz. The filters are built around the IC6A/B which is also an output buffer. A potentiometer is placed in every output to aid in the adjustment and regulation of loudspeakers and amplifiers. The supplied power in the circuit is 15 V and every output can drive a single power amplifier.
List Compoment
R1-2-7-8-12-13-18-19-20 : 47Kohm
R3-4-5-6-21-22-34-35 : 10Kohm
R9-10-11-14-15-16-17 : 15Kohm
R23-24-25-33-36 : 100ohm
R26-27-28-31-32 : 100Kohm
R29-30 : 5.6Kohm
C1-8 : 47uF/25V
C2-7-9-14-23 : 47nF
C3-6 : 1uF/100V
C4-5-10 : 33pF
C11-12-15 : 10uF/25V
C13 : 82nF
C16 : 18pF
C17 : 100pF mini adjustable capacitor
C18 : 2.2nF
C19 : 4.7uF/25V
C20 : 100nF
C21 : 10nF
C22 : 180pF
C24 : 150nF
RV1-RV2 : 2 X 10Kohm Log. pot.
RV3-4 : 10K Log pot.
D1 : 1N4148
IC1-6 : TL072
IC2-3 : TL074
IC4 : MN3101
IC5 : MN3004
This Audio Surround Decoder circuit from www.circuit-projects.com
Rangkaian Charger aki 6 Volt
 Switching transistor T1 is an TIP31C NPN transistor, Si-Power Output/SW, with a TO-220 case and can be changed by using a appropriate substitute such as the NTE291, ECG291, etc. Timer/Oscillator U1 is a 8-pin NE555V and can be changed with a NTE955M or ECG955M. Resistors R4, R5, R6, and R7 are 1% metal film types.
Switching transistor T1 is an TIP31C NPN transistor, Si-Power Output/SW, with a TO-220 case and can be changed by using a appropriate substitute such as the NTE291, ECG291, etc. Timer/Oscillator U1 is a 8-pin NE555V and can be changed with a NTE955M or ECG955M. Resistors R4, R5, R6, and R7 are 1% metal film types. 100Watt Inverter Circuit by IRF44 Mosfet
Absolute Maximum Ratings of IRF44 Mosfet
- Continuous Drain Current (25°C, 10V) = 49 A
- Continuous Drain Current ( 100°C, 10V) = 35 A
- Pulsed Drain Current = 160 A
- Power Dissipation = 94 W
- Gate-to-Source Voltage = ± 20 V
- Avalanche Current = 25 A
- Operating Junction = -55 to + 175
Monday, March 07, 2011
12VDC to 220VAC Inverter Circuit Using IC 555
This is a simple 12VDC to 220AC inverter circuit that can be used produces an AC output at line frequency and 220AC or different voltage by selecting transformer T1. The 555 IC is configured as a low-frequency oscillator, tunable over the frequency range of 50 to 60 Hz by Frequency potentiometer R4.
Input voltage is anywhere from +5V to +15Volt DC, adjust the 2700uF cap's working voltage accordingly. Replacement types for Q1 are: TIP41B, TIP41C, NTE196, ECG196, etc. Replacement types for Q2 are: TIP42B, TIP42C, NTE197, ECG197, etc.
Friday, March 04, 2011
Smoke Detector circuit Using LDR
The diode D1 and D2 in combination drops 1.4 V to give the rated voltage (3.5V ) to UM66 .UM 66 cannot withstand more than 4V.
Car Parking Sensor circuit Using Infra-Red LED
This circuit can be used for an assist in parking the car near the garage wall backing up Pls. LED D7 illuminates Pls bumper-wall distance is about 20 cm., D7 + D6 illuminate at about 10 cm. and D7 + D6 + D5 at about 6 cm. In this manner you are alerted Pls approaching too close to the wall.
Note:
- The infra-red Photo Diode D2, should be of the type incorporating an optical sunlight filter: these components appear in black plastic cases. Some of them resemble TO92 transistors: in this case, please note that the sensitive surface is the curved, not the flat one.
- Avoid sun or artificial light hitting directly D1 & D2.
- If your car has black bumpers, you can line-up the infra-red diodes with the (mostly white) license or number plate.
- It is wiser to place all the circuitry near the infra-red LEDs in a small box. The 3 signaling LEDs can be placed far from the main box at an height making them well visible by the car driver.
- The best setup is obtained bringing D2 nearer to D1 (without a reflecting object) until D5 illuminates; then moving it a bit until D5 is clearly off. Usually D1-D2 optimum distance lies in the range 1.5-3 cm.
R1 : 10K
R2,R5,R6,R9 : 1K
R3 : 33R
R4,R11 : 1M
R7 : 4K7
R8 : 1K5
R10,R12-R14 : 1K
C1,C4 : 1µF/63V
C2 : 47pF
C3,C5 : 100µF
D1 : Infra-red LED
D2 : Infra-red Photo Diode (see Notes)
D3,D4 : 1N4148
D5-7 : LEDs (Any color and size)
IC1 : NE555
IC2 : LM324
IC3 : LM7812
Monday, February 21, 2011
UM3561 - Simple Sound Effects Generator Circuit
This is a very simple. The IC UM3561 produces four differen sound effects, the output at Pin 3 being amplified by the transistor 2N2222. A 64 ohm loudspeaker can be substituted in place of the 56 ohm resistor and 8 ohm loudspeaker.
Note:
The IC sound generator UM3561 is now available in a kt from Maplin Electronics. Click here for the link.
Op-Amp 6-Line Audio Mixer Circuit
The mic inputs are amplified about 100 times or 40dB, the total gain of the mixer including the summing amplifier is 46dB. The mic input is designed for microphones with outputs of about 2mV RMS at 1 meter. Most dynamic microphones meet this standard.
The choice of IC op-amp is not critical in this circuit. Bipolar, FET input or MOS type op-amps can therefore be used; i.e 741, LF351, TL061, TL071, CA3140 etc. The power supply is a dual positive and negative supply, two 9 Volt batteries may be used as shown above or a power supply is recommended for longer periods of use
Water Activated Alarm Using IC 555 Circuit
Probe/contacts may use a non-reactive metal. Gold or silver plated contacts from an old relay May be Used, however a cheap alternative is to wire alternate copper strips from a piece of veroboard. These will eventually oxidize over but as very little current is flowing in the base circuit, the higher impedance the caused by oxidization is not Important. No base resistor is Necessary as the transistor is in emitter follower, current limit being the impedance at the emitter (the oscillator circuit).
Circuit from: www.epanorama.net
Friday, February 11, 2011
LM390 Simple 2-Way intercom Circuit
Triangle and Squarewave Generator Using Op-Amp
 The circuit shows a simple triangle and squarewave generator using a common LM1558 dual op-amp to produce very low frequencies to about 10 KHz. The time interval for one half cycle is about R*C and the outputs will supply about 10mA. Triangle amplitude can be altered by adjusting the 47k resistor and waveform offset can be removed by adding a capacitor in series with the output.
The circuit shows a simple triangle and squarewave generator using a common LM1558 dual op-amp to produce very low frequencies to about 10 KHz. The time interval for one half cycle is about R*C and the outputs will supply about 10mA. Triangle amplitude can be altered by adjusting the 47k resistor and waveform offset can be removed by adding a capacitor in series with the output.
Absolute Maximum Ratings Of Op-Amp LM1558 IC
- Supply Voltage ±22V
- Power Dissipation 400 mW
- Differential Input Voltage ±30V
- Input Voltage (Note 3) ±15V
- Operating Temperature Range −55°C to +125°C
- Storage Temperature Range −65°C to +150°C
- Lead Temperature (Soldering, 10 sec.) 260°C
Sunday, January 23, 2011
Rangkaian Alat Bantu Pendengaran
The heart of the circuit is a constant-volume control amplifier. All the signals picked-up by the microphone are amplified at a constant level of about 1 Volt peak to peak. In this manner very low amplitude audio signals are highly amplified and high amplitude ones are limited. This operation is accomplished by Q3, modifying the bias of Q1 (hence its AC gain) by means of R2.
A noteworthy feature of this circuit is 1.5V battery operation.
List Component
P1 : 22K Log. PotentiometerCircuit from: www.sound.westhost.com
R1,R9 : 10K
R2 : 1M
R3 : 4K7
R4,R7 : 100K
R5 : 3K9
R6 : 1K5
R8 : 100R
C1,C2 : 100nF
C3,C6 : 1µF/63V
C4 : 10µF/25V
C5 : 470µF/25V
D1 : 1N4148
Q1,Q2,Q3 : BC547
Q4 : BC337
MIC1 : electret microphone
SW1 : SPST Switch
J1 : Stereo 3mm. Jack socket
B1 : 1.5V Battery (AA or AAA cell etc.)
Monday, January 10, 2011
30W Mini Mosfet Amplifier
How to Setup of this Amplifier Circuit
- Connect the Power Supply Unit to the Power Amplifier
- Rotate the cursor of R4 fully towards Q1 Collector.
- Set the cursor of R3 to about the middle of its travel.
- Connect a suitable loudspeaker or a 8 Ohm 20W resistor to the amplifier output.
- Connect a Multimeter, set to measure about 50V fsd, across the positive end of C5 and the negative ground.
- Switch on the supply and rotate R3 very slowly in order to read about 23V on the Multimeter display.
- Switch off the supply, disconnect the Multimeter and reconnect it, set to measure at least 1Amp fsd, in series to the positive supply (the possible use of a second Multimeter in this place will be very welcomed).
- Switch on the supply and rotate R4 very slowly until a reading of about 120mA is displayed.
- Check again the voltage at the positive end of C5 and readjust R3 if necessary.
- If R3 was readjusted, R4 will surely require some readjustment.
- Wait about 15 minutes, watch if the current is varying and readjust if necessary.
- 12. Please note that R3 and R4 are very sensitive: very small movements will cause rather high voltage or current variations, so be careful.
- 13. Those lucky enough to reach an oscilloscope and a 1KHz sine wave generator, can drive the amplifier to the maximum output power and adjust R3 in order to obtain a symmetrical clipping of the sine wave displayed.
R1 : 2K2 1/4W Resistor
R2 : 27K 1/4W Resistor
R3,R4 : 2K2 1/2W Trimmers Cermet or Carbon (or 2K)
R5 : 100R 1/4W Resistor
R6 : 1K 1/4W Resistor
R7,R8 : 330R 1/4W Resistors
C1 : 22µF/25V
C2 : 47pF/63V
C3,C4 : 100µF/50V
C5 : 2200µF/50V
Q1 : BC550C NPN Transistor
Q2 : IRF530 N-Channel Hexfet Transistor (or MTP12N10)
Q3 : IRF9530 P-Channel Hexfet Transistor (or MTP12P10)
Circuit From: www.redcircuits.com
9 Volt Portable Headphone Amplifier Circuit

List Component of Portable Headphone Amplifier
P1 = 22KCircuit From: www.redcircuits.com
R1 = 18K
R2 = 68K
R3 = 68K
R4 = 68K
R5 = 18K
R6 = 68K
C1 = 4.7uF/25v
C2 = 4.7uF/25v
C3 = 22pF
C4 = 220uF/25v
C5 = 220uF/25v
C6 = 4.7uF/25v
C7 = 22pF
C8 = 220uF/25v
J1 = 3.5mm Stereo Jack
B1 = 9V Alkaline Battery
IC1 = NE5532 or NE5534
SW1 = SPST Toggle Switch